Welcome to Extea International Co., Ltd.′s official website!
- 86-571-89923671
- carrie.hong@extea.com.cn, hestings@vip.163.com
Welcome to Extea International Co., Ltd.′s official website!
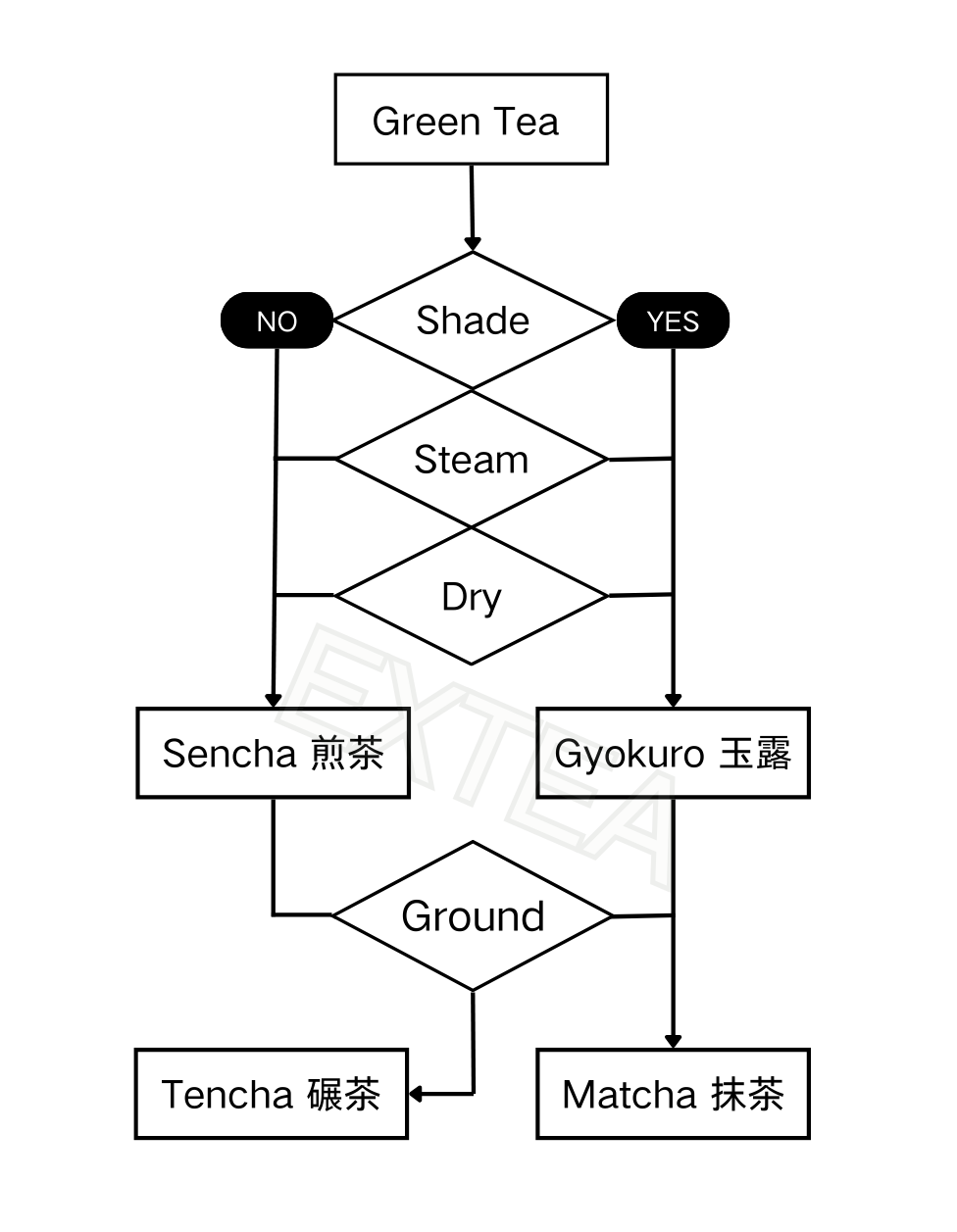
The defining feature of Sencha from other Green Tea is Steaming, as is the usual Japanese style. Chinese styles to process green tea include pan-frying, oven-firing, basket-firing, tumble-drying and sun-drying.
Gyokuro is a kind of Sencha, but shaded when growing.
Tencha is defined by the steaming and grounding process, and thus, it's described as “tea fannings” rather than “leaf tea”.
Matcha is a kind of Tencha, but shaded when growing. Sometimes matcha can be grounded so fine that it looks like “powder”.
Shading is covering green tea from sunlight for about 20-30 days, using covering materials such as reed screens, straw, or shading nets, from the time when the new shoots of the first flush start to grow.
The shading causes both the amino acid L-theanine and the alkaloid caffeine in the tea leaves to increase, and the catechins and tannins to decrease, which yields significant differences from the flavor of sencha. The shading causes the plant to stop converting theanine into catechins to protect itself from UV light. Shading also makes the plant produce more caffeine to protect itself. Gyokuro also has higher chlorophyll content, which accounts for the dark green color of the leaves. These chemical differences lead to unique flavor and aroma of the tea, giving it more umami, a savory sweetness, and less bitterness and astringency. The increased L-theanine content elicits the increased umami taste of gyokuro. It also produces a calming effect which balances out the high caffeine content of gyokuro. Studies on L-theanine indicate that it may also help reduce stress and anxiety and may have neuroprotective effects.
Theoretically, yes, but there is no need to extract from Tencha since the only difference between Tencha and Sencha is the grounding process. The main 2 goals of extraction are: yield of tea solids extracted from the leaf, and concentration of the extract solution. The 6 main steps of extraction are: selection of raw materials, extraction, aroma stripping, tea cream processing, concentration, and drying. Since extraction takes place on tea soup which contains the flavor of camellia sinensis, grounding becomes an irrelevant and expensive process.
P.S. Extea offers Tencha extract. Leave a message if interested.